Translate this page into:
A case report of perennial allergic rhinitis cured with a combined approach in homoeopathy
*Corresponding author: Dr. M. Nagarajan, Department of Organon of Medicine, Dr. Hahnemann Homoeopathy Medical College and Research Center, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India. dr.nagabhms@outlook.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Nagarajan M. A case report of perennial allergic rhinitis cured with a combined approach in homoeopathy. J Intgr Stand Homoeopathy. 2024;7:115-21. doi: 10.25259/JISH_43_2023
Abstract
Allergic conditions such as rhinitis disturb patients and compromise their quality of life (QoL). This case report discusses the clinical issues faced by an 11-year-old boy with perennial allergic rhinitis, which was successfully treated with homoeopathy. The homoeopathic treatment relieved his his disease symptoms and improved his QoL considerably within 6 months. This Case Report demonstrates how homoeopathy treats perennial allergic rhinitis and improves the QoL.
Keywords
Allergy
Hypersensitivity
Quality-of-life
Periodic table
Row 4
INTRODUCTION
Allergy is an abnormal medical condition that makes you ill when you eat, touch, or breathe something that does not normally make other people ill.[1] Nearly 40% of the worldwide population has a higher sensitivity to foreign substances leading to allergy.[2] The prevalence of allergic diseases in the industrialised world has risen enormously.[2] Among these, allergic rhinitis affects 10–30% of the population worldwide.[2] Numerous comorbid conditions are associated with allergic rhinitis, such as asthma, otitis media, nasal polyposis, chronic rhinosinusitis,[3,4] and food allergies.[5]
Homoeopathy considers the patient as a whole; prescription is not just based on the disease’s symptoms. For this, it considers both genetic causative factors represented by the constitutional factors[6] and environmental causative factors. The constitutional factors represent the patient’s physical, mental, and general makeup,[6] including peculiar symptoms. Cure represents the complete annihilation of the disease to its whole extent without recurrence.
CASE REPORT
The patient was an 11-year-old boy residing in a village near Salem. He was brought by his parents to the hospital with complaints of recurrent sneezing, coryza, nasal obstruction, and loss of sense of smell for two years. He had continuous sneezing, especially at night and on exposure to open air with watery coryza. Nasal obstruction occurs at night after the sneezing episodes are over, causing sleep disturbance, gasping for breath through his mouth, and dry cough. He falls asleep after midnight due to tiredness with the mouth open and grinding the teeth on and off.
Life space
His parents narrated that since childhood he has been a very lazy boy and does not even go to play outside with his friends. He is very dull in the evening after coming from school. He sits at home and watches TV even after his mother scolds him for this. In school, his performance is below average. During examinations or questions, he says he cannot recollect what he has studied. His teachers often complain to his mother about his lack of physical activity. He avoids physical training and exercise at school by claiming that he faints while playing.
When asked why he does not play outside, the patient said he prefers to be at home; when he plays with his friends, they bully and beat him. He said they are very strong, and he cannot face them. He feels safe at home, as they cannot come there to beat him. Once, he mentioned this to his father, and the father argued with the other kids’ parents their neighbours. After that, all his friends were angry with him. Since then, he always stays at home.
While the case taking was going on, the patient was constantly shaking his legs throughout. When the physician enquired about this, his parents narrated that he used to do this always, even at home. Even after several scoldings from his father, he did not stop this habit.
Physical generals
Reduced appetite; eats less food but takes more junk foods. Thirst reduction takes 1–1.5 L/day. Hard stools, but passes regularly daily. Urine 4–6 times/24 h, normal. Profuse sweat on palms and soles. Sleep disturbed due to loss of breath. Sleep late, unrefreshed. The mouth opens and grinds teeth on and off during sleep. Thermals: Chilly.
Medical history
Took allopathic treatment with temporary relief.
Family history
Nil.
CLINICAL FINDINGS
ENT examination
Ear: Normal on inspection; Nose: Externally normal; internally, nasal mucosa was severely congested and reddish with the discharge of thin, watery mucus. There is no visible mass or polyp. Throat: fauces appear red and congested with dryness of the mouth.
PNS examination
No tenderness was felt over all sinuses.
Skin
On inspection profuse3+, cold sweat on both palms and soles.
Respiratory system/cardiovascular system/central nervous system/gastrointestinal tract/locomotor
Clinically normal.
DIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT
CBC (28-10-2017) [Figure 1].
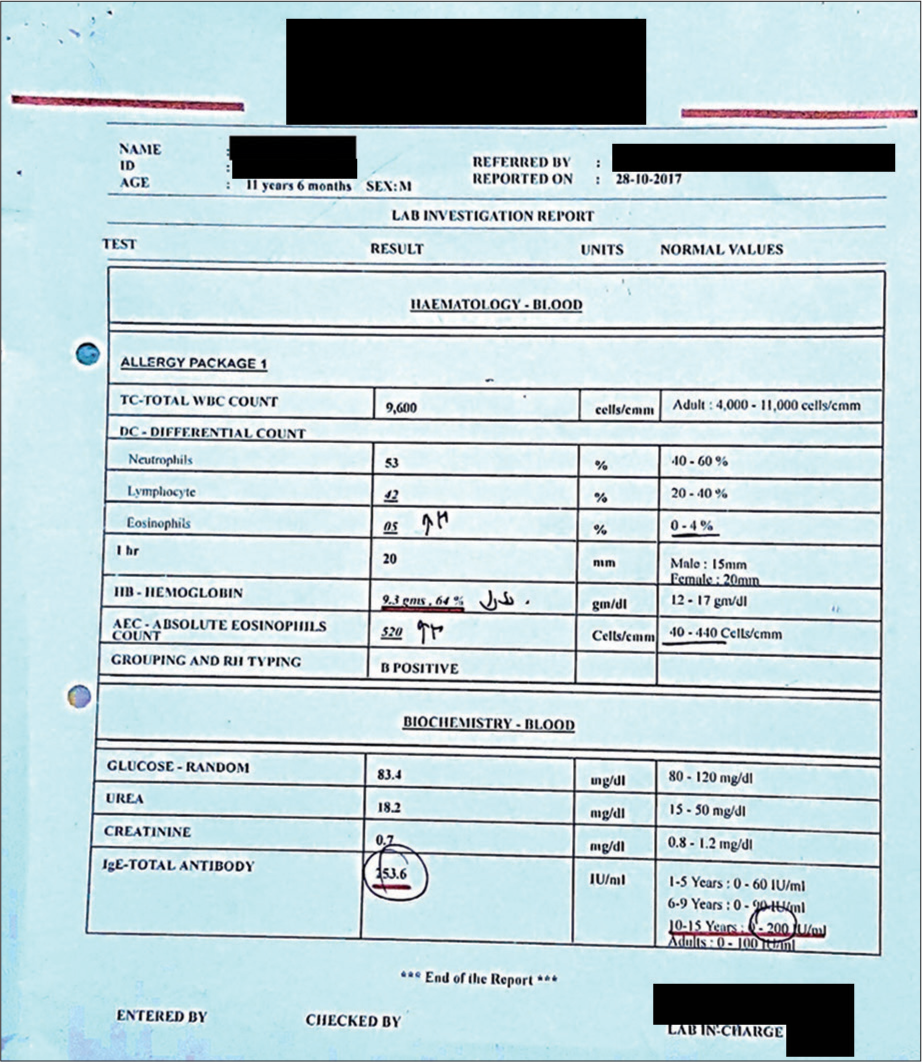
- Diagnostic assessment – before treatment.
THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION
Analysis and evaluation of symptoms
Since the case contains qualified generals and particulars, the Kentian method of evaluation was used.
-
Mental generals:
Will – Laziness3+
Intellect – Dullness in the evening3+
Memory – Weakness of memory3+
-
Physical generals:
Chilly patient3+
Desires snacks with reduced appetite
Reduced thirst
Hard stools
Profuse sweat on palms and soles3+
Grinding teeth3+ and open mouth3+ during sleep
Particulars:
Coryza < night, open air3+
Nasal obstruction < night, cold air3+
Dry cough3+ at night
Shaking of legs3+
Totality of symptoms
Laziness3+
Dullness in the evening3+
Weakness of memory3+
Chilly patient3+
Profuse sweat on palms and soles 3+
Grinding teeth3+ and open mouth3+ during sleep 7. Night aggravation, in general 8. Coryza < open air3+
Nasal obstruction < cold air3+
Dry cough3+
Shaking of legs3+.
Repertorial totality
Laziness
Dullness in the evening
Weakness of memory
< night in general
Coryza, open air, agg
Nasal obstruction, cold air, agg
Teeth, grinding, sleep, during
Mouth, open, sleep, during
Dry cough
Profuse sweat in palms and soles
Fidgeting of lower limbs.
The case has been repertorised using RADAR 10 software in Synthesis Repertory 9.0 version since both generals and particulars are well represented in this repertory.
Repertorial analysis
The repertorial result is shown in [Figure 2].
Sulfur: -22/10
Merc. Sol: -20/10
Nux. Vom: -20/10
Phosphorous: -20/9
Calc carb: -19/9,
Kali carb: -18/9
Pulsatilla: -18/9 and
Dulcamara: -15/9 – were the leading remedies of the repertorisation covering most of the rubrics after proper evaluation
Thermal relation – chilly was taken as the potential differential field, eliminating Sulphur, Merc. sol, and Pulsatilla.
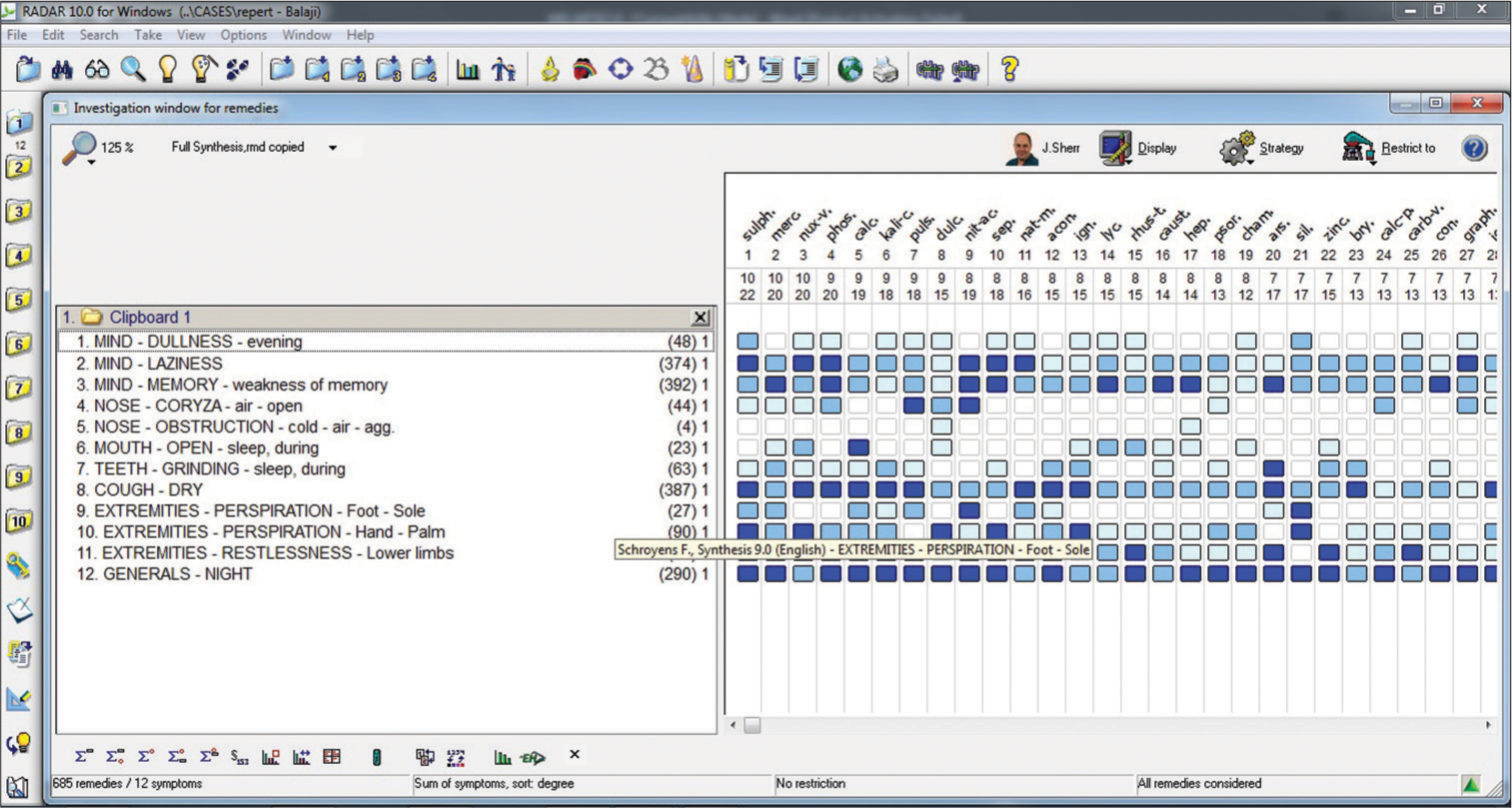
- Repertorisation result.
Selection of remedy based on the classical approach
The characteristic features of Merc sol, such as hurriedness and violent impulses, contradict the patient’s nature despite the night aggravation.
The typical workaholic nature of Nux vomica does not suit the patient’s behaviour, although he is chilly.
The lively, sympathetic, and friendly nature of phosphorus is not present in our patient as he is dull and prefers to be alone in his home, although he is chilly.
The duty-conscious, workaholic, company-desiring nature of Kali-carb does not suit our patient, although he is chilly.
Typical change of weather, cold, damp or rainy weather agg, is not present in the patient. This rules out Dulcamara.
The patient was lazy and the reason he gave was fear of going out of home on account of getting injured or bullied. He feels home is a very secure place. Hence, Calcarea. Carb suits the patient.
Selection of remedy based on the periodic table approach
Calcarea is under Row 4 of the periodic table, and the main issue of row 4 is SECURITY
The remedies on the left-hand side of the row, that is, Kali and Calcarea lack the foundation of security and are hence dependent on others for security. This is further confirmed in the repertorisation chart as Calc-carb is followed by Kali-carb in this case. The remedies on the middle and right of the row represent well-founded security
Calcareas are a step ahead of Kali in dependency, where they run to their support systems in case of the slightest external threat. The main theme of Calc-carb is the need for protection[5]
In addition, the symptoms of profuse perspiration in palms and soles, worse from cold air, forgetfulness, fear, and lethargy are mentioned in high grades in the description of Calc-carb in the materia medica. Thus, Calcarea carb was preferred as the similimum for the patient
The prescription was made by combining the classical and contemporary approaches in homoeopathy. This utilised every available resource from past to present, which increased confidence in our prescription.
Prescription
01 November 2017
(1) Calcarea carb 200 C/1 drop in 100 mL aqua OD/5 mL in aqua in the morning on an empty stomach after five succussions
(2) Placebo/twice a day for three weeks.
Justification of dose and repetition
Being a perennial and episodic disease, administration of dry doses for one time and wait and watch method may not suit this condition. Therefore, daily regular administration of medicine in water doses as per the 5th edition of Organon was suggested and prescribed in this case.
FOLLOW-UP AND OUTCOMES
The follow-up of the case has been summarized as table for easy reference [Table 1 and Figures 3 and 4].
| Follow-up date | Symptoms | Prescription | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 December 2017 | Sneezing reduced; nose block at night reduced; can sleep better; anosmia still present; coryza and dry cough occasionally; Dullness – present; activity – lazy Appetite – improved; thirst – reduced; hard stools present; profuse sweat reduced |
(1) Calcarea carb 200/1 dose in 100 mL aq./OD/5 mL/5 succussion (2) Placebo/BID for 2 weeks |
There was an improvement. Hence, a water dose of the same potency is repeated again. |
| 15 December 2017 | Sneezing reduced; nose block occurred severely for 3–4 days; sleep disturbed; can able to smell mild odours; coryza reduced; dry cough present; Dullness – reduced; activity – lazy Appetite – improved; thirst – reduced; hard stools present; profuse sweat reduced |
1) Calcarea carb 200/1 dose in 100 mL aq./OD/3 mL/10 succussions (2) Placebo/BID for 2 weeks |
There was an initial aggravation, so the quantity of medicine was reduced, and the number of succussions was increased. |
| 02 January 2018 | Sneezing reduced; nose block reduced; sleep better; can smell better; coryza present; dry cough absent. Dullness – reduced; activity – lazy Appetite – improved; thirst – improved; hard stools present on and off; profuse sweat reduced |
(1) Placebo/BID/2 weeks | Improvement present |
| 20 January 2018 | Sneezing and coryza started again on taking ice creams at night; sleep disturbed by nose block again; smell regained to normal; dry cough present Dullness – reduced; activity – started to play with siblings. Appetite – improved; thirst – normal; hard stools once a week; profuse sweat reduced |
(1) Calcarea carb 200/1 dose in 100 mL aq./OD/5 mL/10 succussions (2) Placebo/BID for 2 weeks |
Exciting cause present; so, medicine started to continue again. |
| 02 February 2018 | Sneezing and coryza reduced; sleep disturbed; dry cough present Dullness – present; activity – plays with siblings Appetite/thirst/stool – normal; profuse sweat present |
(1) Calcarea carb 200/1 dose in 100 mL aq./BID/5 mL/15 succussions (2) Placebo/BID for one month |
Standstill condition; so, repetition and succussions increased |
| 03 March 2018 | Sneezing and coryza reduced further; sleep better; no dry cough Dullness – reduced; activity in school appreciated. Plays with siblings Profuse sweat present |
(1) Calcarea carb 200/1 dose in 100 mL aq./BID/5 mL/15 succussions (2) Placebo/BID for one month |
Improvement; so, medicine continued in water dose |
| 25 March 2018 | Sneezing present in the early morning after exposure to cold air; no nose block; no cough; sleep – normal Dullness – much reduced; activity – improved in school and home Sweat reduced |
(1) Calcarea carb 200/1 dose in 100 mL aq./BID/5 mL/15 succussions (2) Placebo/BID for one month |
Moderate improvement is present; medicine continued. |
| 13 April 2018 | Sneezing and nose block reduced; sleep – much better. Dullness absent; can get along with his friends easily; plays well; sweat – normal | (1) Placebo/OD for one month |
Marked improvement present; medicine stopped |
| 23 May 2018 | Sneezing occurs very rarely; no nose block; no other complaints later P/G: Normal. The blood test was taken, and normal reports |
(1) Placebo/OD for 15 days and to discontinue | Marked improvement present; medicine stopped |

- After treatment-absolute eosinophil count.

- After treatment – immunoglobulin E.
DISCUSSION
The case has been evaluated with the Modified Naranjo Criteria for Homoeopathy – MONARCH (Causal attribution Inventory) to assess the relatability of the therapeutic intervention [Table 2]. The obtained score was 11, which led us to believe that the therapeutic effectiveness is more evident in this case.
| Domain | Question | Answer | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Was there an improvement in the main symptom or condition for which homoeopathic medicine was prescribed? | Yes | +2 |
| 2. | Did the clinical improvement occur within a plausible timeframe relative to the medicine intake? | Yes | +1 |
| 3. | Was there a homoeopathic aggravation of symptoms? | Yes | +1 |
| 4. | Did the effect encompass more than the main symptom or condition (i.e., were other symptoms not related to the main presenting complaint improved or changed)? | Yes | +1 |
| 5. | Did overall well-being improve? (Suggest using a validated scale or mention about changes in physical, emotional, and behavioural elements) | Yes (patient’s laziness and dullness improved remarkably; his fear got reduced; he can get along with his friends easily after treatment) | +1 |
| 6A. | Direction of cure: Did some symptoms improve in the opposite order of the development of symptoms of the disease? | No | 0 |
| 6B. | Direction of cure: Did at least one of the following aspects apply to the order of improvement of symptoms: – From organs of more importance to those of less importance? – From deeper to more superficial aspects of the individual? – From the top downwards? | Yes | +1 |
| 7. | Did ‘old symptoms’ (defined as non-seasonal and non-cyclical symptoms that were previously thought to have resolved) reappear temporarily during the course of improvement? | No | 0 |
| 8. | Are there alternative causes (i.e. other than the medicine) that – with a high probability – could have produced the improvement? (consider the known course of disease, other forms of treatment, and other clinically relevant interventions) | No | +1 |
| 9. | Was the health improvement confirmed by any objective evidence? (e.g., investigations, clinical examination, etc.) | Yes | +2 |
| 10. | Did repeat dosing, if conducted, create similar clinical improvement? | Yes | +1 |
| Total score obtained | 11 |
Before treatment, the patient was unable to sleep peacefully and unable to cope with his life, studies, or environment.
Homoeopathic medicine brought a positive change in the patient’s complaints as well as his entire personality. After the prescription, he gradually got over his laziness, dullness, and fear.
The patient has been under observation to date; he now mingles with his friends freely and is not fearful or lazy anymore. Now, his external threat and need for security have vanished from his mind. Therefore, he can move on easily and mingle with his friends. He is now able to study and remember his subjects.
Homoeopathy, as an individualised system of medicine, not only takes care of a person’s disease complaints but also improves his quality of life enabling one to achieve his highest purpose of existence, as mentioned by Dr. Hahnemann in the Organon. Non-recurrence of the complaints for the past two years, along with normal blood parameters, suggests that he is cured at present leading a healthy life. This case report provides evidence that homoeopathy has a wide scope in allergic disorders. However, it would not be appropriate to generalize the usefulness of homoeopathy in cases of allergic rhinitis, on the basis of a single case report. Therefore, rigorous observational and high-quality randomized control studies with larger sample sizes are suggested to ascertain the result obtained in the present case report.
CONCLUSION
Homoeopathy has a good role in treatment of allergic rhinitis in children.
Acknowledgment
I solemnly acknowledge and thank the trust and support given by the parents of this patient towards homoeopathy and me. They have followed all my instructions of taking medicines and restrictions meticulously during the treatment period.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Oxford English-English-Tamil dictionary Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2009. p. :36.
- [Google Scholar]
- Available from: https://www.aaaai.org/about-aaaai/newsroom/allergy-statistics [Last accessed on 2023 May 23]
- Epidemiology of allergy. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2011;44:537-48.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allergic rhinitis and inflammatory airway disease: Interactions within the unified airspace. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010;24(Suppl 4):249-54.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- National prevalence and risk factors for food allergy and relationship to asthma: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(Suppl 4):798-806.e13.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Predictive homoeopathy part I theory of suppression (6th ed). Mumbai: Preeti Vijaykar; 2008. p. :67-75.
- [Google Scholar]






